MCP Server (Preview)
This integration is in Preview mode and is not covered by the Syntasso SLA. If you are evaluating or using it, contact Syntasso to discuss applicability and expectations.
Background
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an emerging open-standard for defining how AI clients can speak to backend services. Moving beyond static API connections where each update needs to be registered with the AI client, MCP connections provide dynamic discovery of new offerings from the connection.
When you invest in Promises as a standard for your platform APIs, you want your user's AI clients to immediately onboard and discover these new capabilities. With the MCP extension for Syntasso Kratix Enterprise you can run your own remote MCP server which connects to your bespoke platform APIs and exposes them in a standard and secure way to your customer AI clients such as Claude and OpenAI.
This integration provides you a personalised MCP server to interrogate and work with your specific platform, all still protected by your platform approved Promise workflows.
Prerequisites
To get started, you will need a SKE Token. You can request a token via the Syntasso website by clicking the "Try SKE Today" button.
In addition, you will need:
- Claude Desktop (Note: reach out for support for other clients)
- The settings config file needs to exist.
On a mac, this will be
~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json - Make
Installing the server
This server can be installed locally or in Kubernetes. These instructions are to install and connect to a local instance.
Download the latest release and untar locally. Enter the release directory from your
terminal and run make install-claude. This will update your Claude Desktop
developer settings
to include the SKE MCP Server.
Close and re-open Claude Desktop to reload the configuration.
Querying your platform
This server depends on access to the Kubernetes cluster that is running Kratix. The
default configuration file used is $HOME/.kube/config but this can be overridden
with the $KUBECONFIG environment variable.
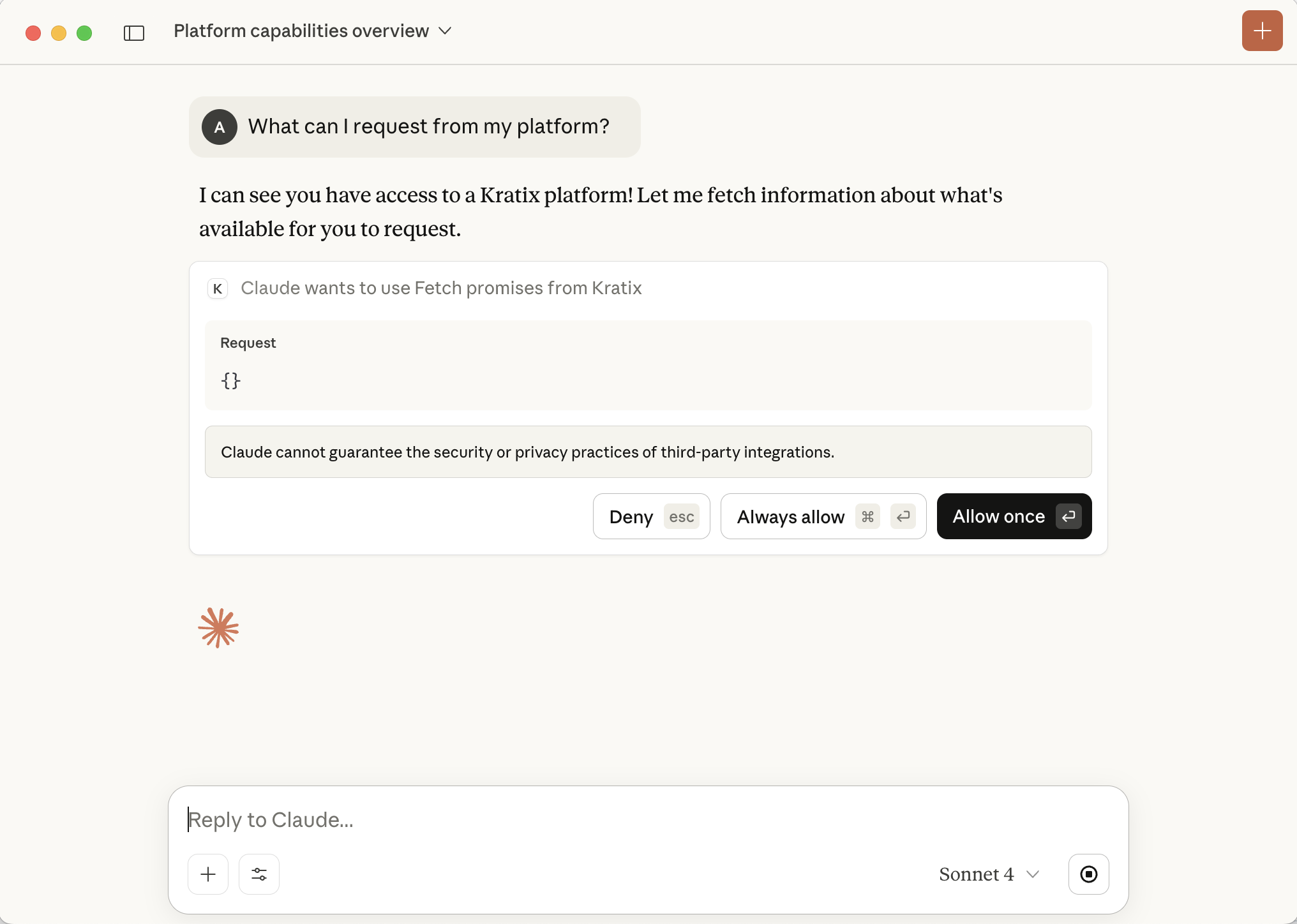
The key tools provided include:
- kratix_health
- list_namespaces
- get_destination_contexts
- list_destinations
- get_ready_destinations
- list_promises
- get_promise
- get_promise_spec_schema
- fetch_destination_contexts
- fetch_ready_destinations
- fetch_full_promises
- fetch_promises
- fetch_promise
- fetch_promise_input_schema
- validate_promise_request
- submit_promise_request
With these, you can ask questions like:
- What can I request from my platform?
- What namespaces do I have <insert Promise type> resources?
- What destinations can I deploy my <insert Promise type> to?
- I need a <insert Promise type>, what can I configure?
Debugging the server
You may want to interrogate the server without Claude Desktop. This is possible with MCP
Inspector which you can run with make dev. Once the site is loaded, make sure the
Transport Type is set to STDIO and connect to the server and use the tools provided.